Click on a section below to see information on the most-requested subjects in the water department.
Water Leaks
High water usage? You might have a leak.
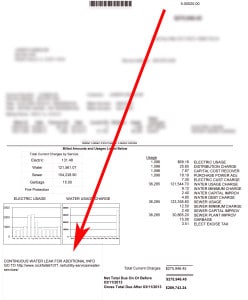 Your water bill will indicate that you have an “intermittent leak” or a “continuous leak”.
Your water bill will indicate that you have an “intermittent leak” or a “continuous leak”.
 You can also look at your meter to determine if you have a leak (see image to the below).
You can also look at your meter to determine if you have a leak (see image to the below).
- Sensus meter: This meter has dials with a black triangle or a red circle, which indicates water movement through the meter. If the triangle or circle is turning slowly. you have a leak.
- Neptune meter: You will need a flashlight to activate the screen on this digital meter by pointing the light towards the top of meter. The meter will indicate flow with an arrow. Blinking faucet indicates an intermittent Leak (on and off) leak and a solid faucet indicates a contentious leak (steady).
Download our PDF to help troubleshoot your leak.
Water Meters
Water Conservation
Here’s a helpful site with tips to conserve water.
Boil Orders
When is a boil order issued?
A boil order is issued by a water system when technical/physical problems in the water have increased the possibility of bacteriological contamination.
In general, a boil order must be issued anytime the pressure in the water system falls below 20 psi. The most common cause of a boil order is a water main break that results in the loss of pressure in the system. Boil orders are also issued when repairs on a fire hydrant, water main or valve result in shutting of the water supply to our customers.
How do I know if my home is under a boil order?
The City makes every attempt to notify all customers involved in the event of a boil order. If the area shut down is relatively small (couple of blocks or so), all homes and/or businesses are tagged in red colored Door knocker on the front door with the date and duration of the shutdown and Facebook. If the area shutdown is larger, a press release is sent to the radio, Television stations, newspaper, and Facebook. The boil order boundaries are also posted on the website.
How long does a boil order last?
Each boil order situation is different making it difficult to predict how long the boil order will be in effect. Once the break or repair is complete, a water sample will be analyzed for the presence of bacteria. The boil order will not be lifted until testing shows the water meets public health standards. The analysis takes a minimum duration of a boil order is 24 hours. A green colored doorknocker tag will be placed on your door once the City is notified that the sample is good no bacteria. In the event of a larger outage, the City will inform the media when the boil order can be lifted
How can I make my water safe?
During a boil order, boiling the water is the best way to ensure that it is free of the illness-causing organisms. Bring water to a boil for a minimum of 5 minutes prior to use. When it cools, refrigerate the water in a clean containers. Boiled water should be used for drinking, ice cubes, brushing teeth, baby’s formula, washing fruits/vegetables, preparing food, preparing coffee, tea, lemonade, etc.
Can I wash my hands using tap water?
It is recommended that you wash your hands using soap and either bottled water or pre-boiled water. An alcohol-based hand sanitizer may also be used.
Can my family take showers or baths using tap water?
The risk of bathing or showering in tap water is uncertain and should be avoided, particularly by people with open wounds or who are immunocompromised. For those who choose to shower or bathe in tap water, minimize time spent in water and be sure to keep eyes and mouth closed. Babies and young children should not bathe or shower in tap water because they often swallow water accidentally.
Can I wash my dishes?
You may use your dishwasher if it has a sanitizing cycle. If unsure, use pre-boiled water for washing your dishes.
What about my coffee maker and ice maker?
None of these devices should be used if they are directly connected to your water supply. Also, filters are unacceptable for removing bacteria. Once you have been notified that the boil order has been lifted, these devices should be cleaned and sanitized according to the operator’s manual for the device.
Can I give my pet’s tap water?
Although pets are not normally affected by the same diseases as humans, caution suggests giving pets pre-boiled or bottled water.
Questions or Concerns?
Ted Padilla
Water Superintendent
815-622-6502
Water Hardness
Hard water is water that has high mineral content (in contrast with “soft water”). Hard water is formed when water percolates through deposits of limestone and chalk, which are largely made up of calcium and magnesium carbonates
Indications of Hard Water
Hard water interferes with almost every cleaning task from laundering and dishwashing to bathing and personal grooming. Clothes laundered in hard water may look dingy and feel harsh and scratchy. Dishes and glasses may be spotted when dry. Hard water may cause a film on glass shower doors, shower walls, bathtubs, sinks, faucets, etc. Hair washed in hard water may feel sticky and look dull. Water flow may be reduced by deposits in pipes.
Hard Water Effects on Soap
Dealing with hard water problems in the home can be a nuisance. The amount of hardness minerals in water affects the amount of soap and detergent necessary for cleaning. Soap used in hard water combines with the minerals to form a sticky soap curd. Some synthetic detergents are less effective in hard water because the active ingredient is partially inactivated by hardness, even though it stays dissolved. Bathing with soap in hard water leaves a film of sticky soap curd on the skin. The film may prevent removal of soil and bacteria. Soap curd interferes with the return of skin to its normal, slightly acid condition, and may lead to irritation. Soap curd on hair may make it dull, lifeless and difficult to manage.
When doing laundry in hard water, soap curds lodge in fabric during washing to make fabric stiff and rough. Incomplete soil removal from laundry causes graying of white fabric and the loss of brightness in colors. A sour odor can develop in clothes. Continuous laundering in hard water can shorten the life of clothes. In addition, soap curds can deposit on dishes, bathtubs and showers, and all water fixtures.
Hard Water Effects on Appliances
Hard water also contributes to inefficient and costly operation of water-using appliances. Heated hard water forms a scale of calcium and magnesium minerals that can contribute to the inefficient operation or failure of water-using appliances. Pipes can become clogged with scale that reduces water flow and ultimately requires pipe replacement.
Potential Health Effects
Hard water is not a health hazard. In fact, the National Research Council (National Academy of Sciences) states that hard drinking water generally contributes a small amount toward total calcium and magnesium human dietary needs. They further state that in some instances, where dissolved calcium and magnesium are very high, water could be a major contributor of calcium and magnesium to the diet. Researchers have studied water hardness and cardiovascular disease mortality. Such studies have been “epidemiological studies,” which are statistical relationship studies. While some studies suggest a correlation between hard water and lower cardiovascular disease mortality, other studies do not suggest a correlation. The National Research Council states that results at this time are inconclusive and recommends that further studies should be conducted.
Rock Falls Water Department Water Hardness Test Results as of March 2016
| Calcium | 82 MG/L |
| Hardness | 330 MG/L |
| Magnesium | 31 MG/L |
National Water Quality Standard
| Classification | MG/L |
|---|---|
| Soft | 0-17.1 |
| Slightly Hard | 17.1-60 |
| Moderately Hard | 60-120 |
| Hard | 120-180 |
| Very Hard | 180 and Over |
Rusty Water
 Iron bacteria are small living organisms which naturally occur in shallow groundwater wells. These nuisance bacteria combine iron and oxygen to form deposits of “rust” bacterial cells, and a slimy material that attaches the bacteria to well pipes, pumps, and plumbing fixtures.
Iron bacteria are small living organisms which naturally occur in shallow groundwater wells. These nuisance bacteria combine iron and oxygen to form deposits of “rust” bacterial cells, and a slimy material that attaches the bacteria to well pipes, pumps, and plumbing fixtures.
It is important to note that when rusty water is experienced it is not a health concern but one of aesthetic quality.
Rusty-brown, orange, or light yellow water can be caused by a variety of reasons including:
- Water main breaks
- Fire fighting operations
- Hydrant flushing
- Construction work or damage
- System depressurizations
- Corroding iron pipes
- Routine maintenance
Normally rusty water events dissipate in 4-6 hours but could last longer depending on water usage in the area. If the event lasts more than 24 hours please call our Customer Service Office at 815-622-1115.
If you are experiencing rusty water:
- Do not run your water until it turns clear. It is of little to no value to do so and is wasteful and costly to you as a consumer.
- Use of HOT water should be kept to a minimum, as it will draw cold rusty water into your hot water tank. If your hot water tank does have rust in it, use caution and follow the manufacturer’s directions for shutting down, draining, and re-starting your hot water tank.
- Do not wash laundry. Clothing washed in rusty water can become stained. If this occurs, it is important to NOT dry the clothing. Instead, leave the wet clothing in the washer and apply an iron removal product as soon as possible to prevent the iron stain from setting. Please follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Water Chlorination
Why does the City of Rock Falls Chlorinate the water?
As a halogen, chlorine is a highly efficient disinfectant, and is added to public water supplies to kill disease-causing pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and protozoans, that commonly grow in water supply reservoirs, on the walls of water mains and in storage tanks.
The chlorine odor of tap water can be traced to the chlorine “residual,” a low level of chlorine maintained in water to guard against bacteria, viruses and parasites, which may be in water as it flows from the treatment plant to points of use. In the US, even treatment plants that use non-chlorine disinfection technologies are required to add chlorine to the water before it flows into the distribution system. The chlorine residual acts like a “body guard” for water in transit. As long as there is a residual level of chlorine, the consumer is reasonably protected from harmful microorganisms. According to the AWWA, if the chlorine residual level is sufficient without being excessive, water will not smell like chlorine. Yet, sensitivity to the odor of chlorine varies among consumers. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) requires treatment facilities to maintain a chlorine residual level that is chemically detectable but no greater than 4 mg/l. Four milligrams per liter is the “Maximum Residual Disinfectant Level” for chlorine, and it is the level below which there are no known or expected risks to health from exposure to the disinfectant. Most people can sense a chlorine residual around 1 mg/l. If your water smells strongly of chlorine, it is possible that your treatment facility conveys water over a long distance, requiring heavy chlorination to maintain a chlorine residual throughout the system. (The chlorine residual also may be raised by treatment facilities during warm weather when chlorine dissipates readily from water.) AWWA notes that this can be remedied by systems reducing chlorine added at the point of entry and installing booster chlorination systems in the distribution line. The consumer also has practical options.
The Water Department maintains a 2.0 mg/l combined chlorine at the Water Plant located at the Green Water Tower to ensure that the chlorine residual of .5 ppm is maintained to the very far ends of the distribution system at Clearwater Drive and Harvest Time Church on Dixon Ave. the MCL for Chlorine is 4.0 mg/l Water quality is tested each day 365 days a year at the Water Plant and the distribution system Monday thru Friday. Water samples at the source water and distribution system (10 bacterial samples each set) are taken during the first 15 days of the month and the 2nd set are taken from the 15th day to end of the month. Results are sent to the IEPA monthly or when samples are taken.
How to remove the Chlorine taste and smell?
- Fill a container of water and let it sit for a day. This will allow the chlorine to dissipate and remove the taste and odor but, still receive the nutrients the water provides.
- Add a filtering system on your water supply inside your home. The more expensive the unit, the better the removal. Paper filters will not remove the issue. Charcoal systems or Reverse Osmosis system will remove the taste and odor but, will also remove all the nutrients in the water.
